映射(Map)实现
2024/4/8大约 9 分钟
映射(Map)实现
理解
Map 在有些编程语言中也叫做字典(dictionary,比如 Python、Objective-C、Swift 等)
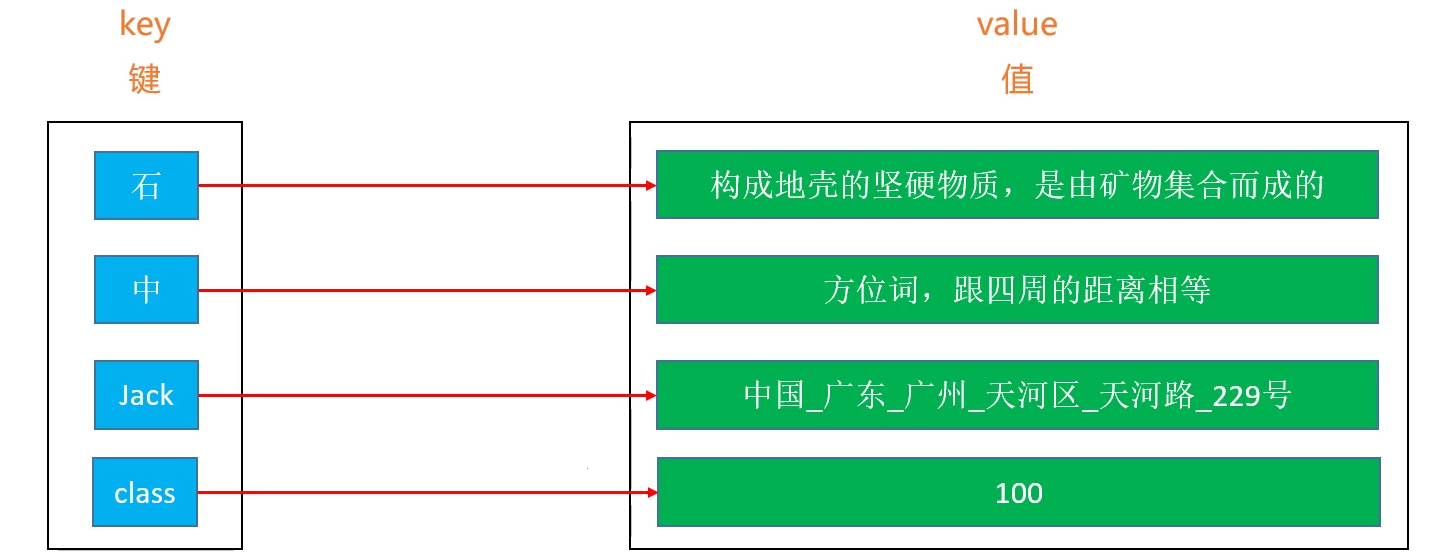
Map 的每一个 key 是唯一的
类似Set,Map可以直接利用链表,二叉搜索树 (AVL树,红黑树)等数据结构来实现
Map 与 Set 的关系
Map 的所有 key 组合在一起,其实就是一个 Set。因此,Set 可以间接利用 Map 来作内部实现
接口设计
public interface Map<K, V> {
int size();
boolean isEmpty();
void clear();
V put(K key,V value);
V get(K key);
V remove(K key);
boolean containsKey(K key);
boolean containsValue(V value);
void traversal(Visitor<K,V> visitor);
public static abstract class Visitor<K,V> {
boolean stop;
public abstract boolean visit(K key,V value);
}
}红黑树实现TreeMap
TreeMap分析
时间复杂度(平均)
- 添加、删除、搜索:O(logn)
特点
Key 必须具备可比较性
元素的分布是有顺序的
在实际应用中,很多时候的需求
Map 中存储的元素不需要讲究顺序
Map 中的 Key 不需要具备可比较性
不考虑顺序、不考虑 Key 的可比较性,Map 有更好的实现方案,平均时间复杂度可以达到 O(1),那就是采取哈希表来实现 Map
实现
/**
* @Description 红黑树实现映射(把TreeMap本身当成一棵红黑树,
* 用key和value代替element,即从头开始用红黑树实现一个Map)
* @author Polaris
* @version
* @date 2020年3月12日下午6:25:57
*/
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked","unused"})
public class TreeMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V>{
private static final boolean RED = false;
private static final boolean BLACK = true;
protected int size;
protected Node<K,V> root;// 根节点
protected Comparator<K> comparator;// 比较器定制排序
public TreeMap() {
this(null);
}
public TreeMap(Comparator<K> comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
}
private static class Node<K,V> {
K key;
V value;
boolean color = RED;
Node<K,V> left; // 左子节点
Node<K,V> right; // 右子节点
Node<K,V> parent; // 父节点
public Node(K key,V value, Node<K,V> parent) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.parent = parent;
}
public boolean isLeaf() {
return left == null && right == null;
}
public boolean hasTwoChildren() {
return left != null && right != null;
}
public boolean isLeftChild() {
return parent != null && this == parent.left;
}
public boolean isRightChild() {
return parent != null && this == parent.right;
}
public Node<K,V> getSibling(){
if(isLeftChild()) {
return parent.right;
}
if(isRightChild()) {
return parent.left;
}
return null;
}
}
/**
* 检查key是否为空
*/
protected void keyNoNullCheck(K key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("key must no be null!");
}
}
@Override
public int size() {
return size;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
@Override
public void clear() {
root = null;
size = 0;
}
@Override
public V put(K key, V value) { //一般只要求key具有可比较性就
keyNoNullCheck(key);
//添加第一个节点(根节点)
if (root == null) {
root = new Node<>(key, value, null);
size++;
afterPut(root);//新添加节点之后的处理
return null;
}
// 如果添加的不是第一个节点:
// 1.找到待添加位置的父节点
Node<K,V> parent = root;
Node<K,V> node = root;
int cmp = 0;
while(node != null) {
cmp = compare(key, node.key);
parent = node;
if (cmp > 0) {
node = node.right;
} else if (cmp < 0) {
node = node.left;
} else {
node.key = key;//一般覆盖(不同对象可能有相同的比较参数)
V oldValue = node.value;
node.value = value;
return oldValue;
}
}
// 2.判断插入父节点的左子节点还是右子节点
Node<K,V> newNode = new Node<>(key, value, parent);
if (cmp > 0) {
parent.right = newNode;
} else {
parent.left = newNode;
}
size++;
afterPut(newNode);//新添加节点之后的处理
return null;
}
private void afterPut(Node<K,V> node) {
Node<K,V> parent = node.parent;
//添加的是根节点 或 上溢到根节点
if(parent == null) {
black(node);
return;
}
//类型一:parent是黑色(不用处理四种情况)
if(isBlack(parent)) return;
//类型二:parent是红色且uncle是红色(会上溢的四种情况)
Node<K,V> uncle = parent.getSibling();
Node<K,V> grand = red(parent.parent);//以下情况都需要将grand染成红色,可以统一处理
if(isRed(uncle)) {
black(parent);
black(uncle);
//把祖父节点当作是新添加的节点
afterPut(grand);//上溢递归调用
return;
}
//类型三:parent是红色且uncle不是红色(需要旋转的四种情况)
if(parent.isLeftChild()) {//L
if(node.isLeftChild()) { //LL
black(parent);
} else { //LR
black(node);
rotateLeft(parent);
}
rotateRight(grand);
} else { //R
if(node.isLeftChild()) { //RL
black(node);
rotateRight(parent);
} else { //RR
black(parent);
}
rotateLeft(grand);
}
}
private int compare(K k1, K k2) {
if (comparator != null) {
return comparator.compare(k1, k2);
}
return ((Comparable<K>)k1).compareTo(k2);
}
/**
* 给节点上色
*/
private Node<K,V> color(Node<K,V> node,boolean color) {
if(node == null) return node;
node.color = color;
return node;
}
/**
* 将节点染成红色
*/
private Node<K,V> red(Node<K,V> node){
return color(node,RED);
}
/**
* 将节点染成黑色
*/
private Node<K,V> black(Node<K,V> node){
return color(node,BLACK);
}
/**
* 获取当前节点的颜色
*/
private boolean colorOf(Node<K,V> node) {
return node == null ? BLACK : node.color;
}
/**
* 判断当前颜色是否为黑色
*/
private boolean isBlack(Node<K,V> node) {
return colorOf(node) == BLACK;
}
/**
* 判断当前颜色是否为红色
*/
private boolean isRed(Node<K,V> node) {
return colorOf(node) == RED;
}
/**
* 左旋转,以RR为例
*/
private void rotateLeft(Node<K,V> grand) {
Node<K,V> parent = grand.right;
Node<K,V> child = parent.left;//child就是T1子树
grand.right = child;
parent.left = grand;
afterRotate(grand, parent, child);
}
/**
* 右旋转,以LL为例
*/
private void rotateRight(Node<K,V> grand) {
Node<K,V> parent = grand.left;
Node<K,V> child = parent.right;
grand.left = child;
parent.right = grand;
afterRotate(grand, parent, child);
}
/**
* 抽取左旋转和右旋转中的重复代码
*/
private void afterRotate(Node<K,V> grand,Node<K,V> parent,Node<K,V> child) {
//更新parent的parent(让parent成为子树的根节点)
parent.parent = grand.parent;
if(grand.isLeftChild()) {
grand.parent.left = parent;
} else if(grand.isRightChild()) {
grand.parent.right = parent;
} else { //grand是root节点
root = parent;
}
//更新child的parent
if(child != null) {
child.parent = grand;
}
//更新grand的parent
grand.parent = parent;
}
@Override
public V get(K key) {
Node<K,V> node = node(key);
return node != null ? node.value : null;
}
/**
* 根据key找到对应节点
*/
private Node<K,V> node(K key){
Node<K,V> node = root;
while(node != null) {
int cmp = compare(key,node.key);
if(cmp == 0) return node;
if(cmp > 0) {
node = node.right;
} else {
node = node.left;
}
}
return null;
}
@Override
public V remove(K key) {
return remove(node(key));
}
/**
* 根据key删除节点元素
*/
private V remove(Node<K,V> node) {
if(node == null) return null;
size--;
V oldValue = node.value;
//考虑度为2的节点,转化为度为1
if(node.hasTwoChildren()) {
Node<K,V> s = successor(node);//后继节点
//用后继节点的值覆盖度为2的节点的值
node.key = s.key;
node.value = s.value;
//删除后继节点
node = s;
}
//删除node节点(能到这则说明node的度必为0或1)
Node<K,V> replacement = node.left != null ? node.left : node.right;
if(replacement != null) { //node是度为1的节点
//更改parent
replacement.parent = node.parent;
//更改parent的left,right指向
if(node.parent == null) { //node是度为1的节点也是根节点
root = replacement;
} else if(node == node.parent.left) {
node.parent.left = replacement;
} else { //在右边
node.parent.right = replacement;
}
//此时开始恢复平衡(AVL树 或 RB树需要实现此方法)
afterRemove(node,replacement);
} else if(node.parent == null){ //node是叶子节点也是根节点
root = null;
afterRemove(node,null);
} else { //node是叶子节点但不是根节点
if(node == node.parent.left) {
node.parent.left = null;
} else {
node.parent.right = null;
}
//此时开始恢复平衡(AVL树 或RB树 需要实现此方法)
afterRemove(node,null);
}
return oldValue;
}
/**
* 实现删除节点后的处理操作
*/
private void afterRemove(Node<K,V> node,Node<K,V> replacement) {
//情况一:如果删除的节点是红色,不用处理
if(isRed(node)) return;
//情况二:用于取代node子节点的是红色节点
if(isRed(replacement)) {
black(replacement);
return;
}
//情况三:删除的是黑色叶子节点(下溢)
Node<K,V> parent = node.parent;
//删除的是根节点
if(parent == null) return;
//判断被删除的node的节点是左还是右
boolean left = parent.left == null || node.isLeftChild();
Node<K,V> sibling = left ? parent.right : parent.left;
if(left) { //被删除的节点在左边,兄弟节点在右边(镜像对称处理)
if(isRed(sibling)) { //兄弟节点是红色,就要转成黑色
black(sibling);
red(parent);
rotateLeft(parent);
//更换兄弟
sibling = parent.right;
}
//兄弟节点必然是黑色
if(isBlack(sibling.left) && isBlack(sibling.right)) {
//兄弟节点没有一个红色子节点,父节点要向下向子节点合并
boolean parentBlack = isBlack(parent);
black(parent);
red(sibling);
if(parentBlack) {
afterRemove(parent, null);
}
} else { //兄弟节点至少有 1 个红色节点,就要向兄弟节点借元素
if(isBlack(sibling.right)) {
//兄弟节点的右边不是红色,则兄弟要先旋转
rotateRight(sibling);
sibling = parent.right;
}
color(sibling,colorOf(parent));
black(sibling.right);
black(parent);
rotateLeft(parent);
}
} else { //被删除的节点在右边,兄弟节点在左边(图示的是这种)
if(isRed(sibling)) { //兄弟节点是红色,就要转成黑色
black(sibling);
red(parent);
rotateRight(parent);
//更换兄弟
sibling = parent.left;
}
//兄弟节点必然是黑色
if(isBlack(sibling.left) && isBlack(sibling.right)) {
//兄弟节点没有一个红色子节点,父节点要向下向子节点合并
boolean parentBlack = isBlack(parent);
black(parent);
red(sibling);
if(parentBlack) {
afterRemove(parent, null);
}
} else { //兄弟节点至少有 1 个红色节点,就要向兄弟节点借元素
if(isBlack(sibling.left)) {
//兄弟节点的左边不是红色,则兄弟要先旋转
rotateLeft(sibling);
sibling = parent.left;
}
color(sibling,colorOf(parent));
black(sibling.left);
black(parent);
rotateRight(parent);
}
}
}
/**
* 利用中序遍历求某个节点的前驱节点
*/
private Node<K,V> predecessor(Node<K,V> node) {
if(node == null) return null;
//前驱节点在左子树中:node.left.right.right...
Node<K,V> p = node.left;
if(p != null) {
while(p.right != null) {
p = p.right;
}
return p;
}
//从祖父节点中寻找前驱节点
while(node.parent != null && node == node.parent.left) {
node = node.parent;
}
//情况一:node.parent == null ↓
//情况二:node == node.parent.right ↓
return node.parent;
}
/**
* 利用中序遍历求某个节点的后继节点
*/
private Node<K,V> successor(Node<K,V> node) {
if(node == null) return null;
//前驱节点在右子树中:node.right.left.left...
Node<K,V> p = node.right;
if(p != null) {
while(p.left != null) {
p = p.left;
}
return p;
}
//从祖父节点中寻找前驱节点
while(node.parent != null && node == node.parent.right) {
node = node.parent;
}
//情况一:node.parent == null ↓
//情况二:node == node.parent.left ↓
return node.parent;
}
@Override
public boolean containsKey(K key) {
return node(key) != null;
}
@Override
public boolean containsValue(V value) {
if(root == null) return false;
Queue<Node<K,V>> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node<K,V> node = queue.poll();
if(valEquals(value, node.value)) return true;
if(node.left != null) {
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null) {
queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
return false;
}
private boolean valEquals(V v1,V v2) {
return v1 == null ? v2 == null : v1.equals(v2);
}
@Override
public void traversal(Visitor<K, V> visitor) {
if(visitor == null) return;
traversal(root,visitor);
}
private void traversal(Node<K,V> node,Visitor<K, V> visitor) {
if(node == null || visitor.stop) return;
traversal(node.left,visitor);
if(visitor.stop) return;
visitor.visit(node.key, node.value);
traversal(node.right,visitor);
}
}测试
public class TreeMapTest {
@Test
public void test() {
Map<String,Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put("c", 2);
map.put("a", 5);
map.put("b", 6);
map.put("a", 8);
map.traversal(new Visitor<String, Integer>() {
@Override
public boolean visit(String key, Integer value) {
System.out.println(key + "_" + value);
return false;
}
});
}
@Test
public void test2() {
FileInfo fileInfo = Files.read("D:\\Learning\\Java"
+ "\\workspace_eclipse\\workspace001_2019-3"
+ "\\DataStructures\\src\\com\\polaris4"
+ "\\map",
new String[]{"java"});
System.out.println("文件数量:" + fileInfo.getFiles());
System.out.println("代码行数:" + fileInfo.getLines());
String[] words = fileInfo.words();
System.out.println("单词数量:" + words.length);
Map<String, Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < words.length; i++) {
Integer count = map.get(words[i]);
count = (count == null) ? 1 : (count + 1);
map.put(words[i], count);
}
map.traversal(new Visitor<String, Integer>() {
public boolean visit(String key, Integer value) {
System.out.println(key + "_" + value);
return false;
}
});
}
}public class Files {
/**
* 读取文件内容
* @param file
* @return
*/
public static FileInfo read(String file) {
if (file == null) return null;
FileInfo info = new FileInfo();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
try (FileReader reader = new FileReader(file);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(reader)) {
String line;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
sb.append(line).append("\n");
info.setLines(info.getLines() + 1);
}
int len = sb.length();
if (len > 0) {
sb.deleteCharAt(len - 1);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
info.setFiles(info.getFiles() + 1);
info.setContent(sb.toString());
return info;
}
/**
* 读取文件夹下面的文件内容
* @param dir
* @param extensions
* @return
*/
public static FileInfo read(String dir, String[] extensions) {
if (dir == null) return null;
File dirFile = new File(dir);
if (!dirFile.exists()) return null;
FileInfo info = new FileInfo();
dirFile.listFiles(new FileFilter() {
public boolean accept(File subFile) {
String subFilepath = subFile.getAbsolutePath();
if (subFile.isDirectory()) {
info.append(read(subFilepath, extensions));
} else if (extensions != null && extensions.length > 0) {
for (String extension : extensions) {
if (subFilepath.endsWith("." + extension)) {
info.append(read(subFilepath));
break;
}
}
} else {
info.append(read(subFilepath));
}
return false;
}
});
return info;
}
}public class FileInfo {
private int lines;
private int files;
private String content = "";
public String[] words() {
return content.split("[^a-zA-Z]+");
}
public int getFiles() {
return files;
}
public void setFiles(int files) {
this.files = files;
}
public int getLines() {
return lines;
}
public void setLines(int lines) {
this.lines = lines;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
public FileInfo append(FileInfo info) {
if (info != null && info.lines > 0) {
this.files += info.files;
this.lines += info.lines;
this.content = new StringBuilder(this.content)
.append("\n")
.append(info.content)
.toString();
}
return this;
}
}